Zambia

























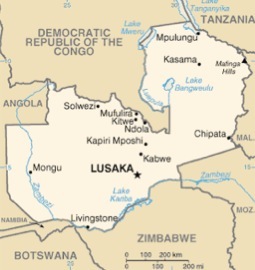

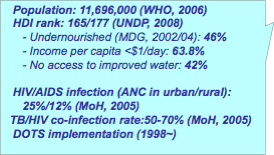
In Zambia all forms of notified TB cases remained constant at approximately 100/100,000 population between 1964 and 1984. However the case detection rate increased from 100 to 400/100,000 population during the period of 1985-96 (CBoH Health Demographic Survey). The incidence rate of tuberculosis (all forms) in Zambia is 553 per 100,000 populations with the total number of incidence amounting to 64,632 (WHO, 2006). The TB burden in the capital city Lusaka is the highest in the country: 28.3% (MoH, Report of the review of NTCP of Zambia, 2005).
The fivefold increase of the TB case notification rate since early 1990s is strongly affected by the occurrence of HIV/AIDS. The overall HIV/AIDS prevalence in Zambia was reported as 15.6% (Zambia demographic and health survey 2003) and TB is a leading cause of death in people with HIV/AIDS. HIV prevalence among TB patients (TB/HIV prevalence) was reported to as 83.2% in 1999 (UNAIDS/WHO 2004) that indicates high risk of TB/HIV co-infection cases.
Background
Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) Project (2001-2007): TB and HIV/AIDS Control

Since 2001 the project aimed to develop a high quality TB examination system that could be model for the national TB examination network. For that purpose it established an EQA (External Quality Assurance) system for smear examination, conducted baseline survey for EQA, developed “National Guidelines for EQA on sputum microscopy, training materials for smear examinations, and TB/HIV operational research in the target communities.
Laboratory System Strengthening Under TBCAP (2006~)
Under the USAID funded Tuberculosis Control Assistance Program (TBCAP) in Zambia, RIT/JATA is involved as a collaborative organization in achieving the following objectives to: (1) strengthen and expand quality DOTS in all five provinces in five years; (2) improve the collaboration between TB and HIV; (3) increase community involvement; and (4) strengthen public and private partnership.
RIT/JATA is responsible for the human resources management for the laboratory system through supervising lab experts and providing training. RIT/JATA also serves as a TBCAP member in Zambia Steering Committee to provide technical and programmatic guidance.
TB/HIV Community DOTS Programme (2008~)
Target:
- A population of 65,000 people living in Bauleni compound, Lusaka District (urban)
Overall aim:
- To reduce the spread of TB/HIV infection through holistic care and support to TB/HIV infected/affected households with pro-poor approach
Objectives (within 1 year):
- To reduce the spread of both TB and HIV infection through detecting TB, applying active case finding management and providing DCT counseling and HIV testing service
- To increase the number of case detection for TB positive by 1.5 times
- To increase the number of TB positive tested for HIV up to 70%
Project components:
- ACFM (Active Case Finding Management). Provide free and sensitive diagnosis at early stage and counseling service for TB/HIV through ACFM
- Conduct training workshop for TB Treatment Supporters on TB/HIV related care and support, HBC and nutrition to enhance knowledge and skills of TS
- Improve the successful treatment completion rate and reduce defaulter rate amongst through TB DOT supervision with or without ART
- Improve livelihoods of TB/HIV affected households and TB treatment supporters through home gardening, revolving fund (micro-credit)
“JAZ-ACTIVE”
(JATA-ZATULET Active Case Finding of Tuberculosis Involving Volunteers Empowerment)




2009 Copyright © Research Institute of Tuberculosis/JATA All Rights Reserved.